- 全部删除
 您的购物车当前为空
您的购物车当前为空
购物车
ANGPTL
(1)
ATP Citrate Lyase
(11)
Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase
(15)
Aconitase
(1)
Acyltransferase
(45)
Adenosine Deaminase
(8)
AhR
(26)
Amino Acids and Derivatives
(46)
Aminopeptidase
(19)
Amylase
(9)
Angiotensin-converting Enzyme (ACE)
(18)
Apolipoprotein
(5)
CETP
(14)
CPT
(4)
Calcium Channel
(391)
Carbonic Anhydrase
(78)
Casein Kinase
(69)
Cytochromes P450
(237)
DHFR
(31)
Decarboxylase
(7)
Dehydrogenase
(223)
Drug Metabolite
(128)
Endogenous Metabolite
(1572)
Epoxide Hydrolase
(26)
FAAH
(42)
FABP
(7)
FXR
(44)
Factor Xa
(37)
Fatty Acid Synthase
(43)
GSNOR
(2)
Glucokinase
(44)
Glucosidase
(91)
Glutathione Peroxidase
(40)
Glyoxalase
(2)
HIF/HIF Prolyl-Hydroxylase
(77)
HMG-CoA Reductase
(34)
HSP
(123)
Hexokinase
(4)
Hydrogenase
(1)
Hydroxylase
(28)
IDO
(23)
Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase (IDO)
(33)
Isocitrate Dehydrogenase (IDH)
(15)
LDL
(24)
Lipase
(26)
Lipid
(19)
Liposome
(26)
Lipoxygenase
(111)
Liver X Receptor
(30)
MAGL
(13)
MAO
(98)
Mitochondrial Metabolism
(92)
N-Acetylglucosaminyltransferase
(1)
NADPH
(34)
NAMPT
(20)
NEDD4-1
(1)
NEDD8
(5)
NUDIX hydrolase
(2)
Neprilysin
(11)
PAI-1
(13)
PDE
(233)
PGC-1α
(3)
PGK1
(1)
PKM
(13)
PPAR
(214)
Phosphatase
(200)
Phospholipase
(110)
Phosphorylase
(15)
Procollagen C Proteinase
(1)
Prolyl Endopeptidase (PREP)
(4)
RAR/RXR
(6)
REV-ERB
(1)
ROR
(39)
Reactive Oxygen Species
(257)
Reductase
(52)
Retinoid Receptor
(57)
SGK
(13)
Serine/threonin kinase
(46)
Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase (SCD)
(13)
Taste receptor
(2)
Thioredoxin
(2)
Transaminase
(3)
Transferase
(71)
Transketolase
(2)
UGT
(12)
Vitamin
(17)
Xanthine Oxidase
(35)
glycosidase
(5)
hCE
(2)
stilbene oxidase
(1)
transporter
(47)
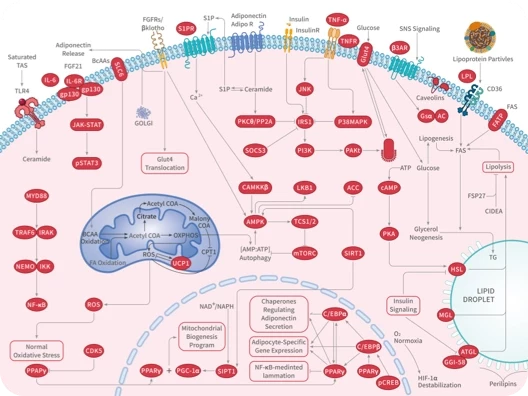
Fatty Acid Synthase
脂肪酸合酶(FAS)是一种在人类中由FASN基因编码的酶。脂肪酸合酶是一种催化脂肪酸合成的多酶蛋白。其主要功能是在NADPH存在下催化乙酰辅酶a和丙二酰辅酶a合成棕榈酸。
Denifanstat
 客户已引用
客户已引用
T152711399177-37-7
Denifanstat (FASN-IN-2) 是一种脂肪酸合成酶 (FASN) 抑制剂 (IC50=0.052 μM,EC50=0.072 μM),具有选择性和口服活性。Denifanstat 已被用于脂肪性肝炎的研究。
- ¥ 696
规格
数量
TVB-3664
T171812097262-58-1
TVB-3664 是一种具有口服具有活力的、选择性的、可逆的、具有高生物利用度的脂肪酸合酶抑制剂,其对人和老鼠棕榈酸酯合成的IC50分别为 18 nM 和 12 nM。可显著抑制微管蛋白棕榈酰化和 mRNA 表达。
- ¥ 1070
规格
数量
VY-3-135
T97321824637-41-3
VY-3-135 是口服有效的、稳定的、特异性乙酰辅酶 A 合成酶 2 (ACSS2)抑制剂,IC50为 44 nM,对重组人 ACSS1 或 ACSS3 未表现出任何抑制活性。VY-3-135 能有效抑制 ACSS2 依赖性脂肪酸代谢,但对肿瘤中的基因表达没有影响。
- ¥ 739
规格
数量
Rimiducid
T14298195514-63-7
Rimiducid 是一种可渗透脂质的他克莫司类似物,是一种二聚剂,通过交联 FKBP 结构域起作用。它将 Caspase 9 自杀开关二聚化并迅速诱导细胞凋亡。
- ¥ 568
规格
数量
Ac-CoA Synthase Inhibitor1
T4380508186-14-9
Ac-CoA Synthase Inhibitor1 (ACSS2 inhibitor) 是一种可逆的醋酸盐依赖性乙酰辅酶 A 合成酶 2 抑制剂,IC50为 0.6 µM,可抑制呼吸道合胞病毒。
- ¥ 259
规格
数量
Orlistat 客户已引用
客户已引用
T068696829-58-2
Orlistat (Tetrahydrolipstatin) 是一种脂肪酶 (lipase) 抑制剂,也是一种脂肪酸合成酶 (FASN) 抑制剂。Orlistat 具有促减肥的作用。
- ¥ 748
规格
数量
C75 客户已引用
客户已引用
T10657218137-86-1
C75 是一种合成脂肪酸合酶 (FASN) 抑制剂,可抑制前列腺癌细胞 PC3 (IC50: 35 μM)。C75 增加 CPT1 活性,降低 DIO。
- ¥ 387
规格
数量
ACSS2-IN-2
T600602332820-04-7
ACSS2-IN-2 (MTB-9655) 是酰基辅酶 A 合成酶短链家族成员 2 (ACSS2) 抑制剂。ACSS2-IN-2 可抑制 ACSS2 活性,IC50 为 3.8 nM。ACSS2-IN-2 可用于多种疾病的研究,如病毒感染、代谢紊乱、神经精神疾病、炎症 自身免疫疾病和癌症。
- ¥ 495
规格
数量
FASN-IN-1
T112671808260-84-5In house
FASN- in -1是一种有效的、特异性的脂肪酸合成酶(FASN)抑制剂,是一种专门设计用于靶向和抑制FASN 活性的化合物,是一种参与脂肪酸合成的酶,可抑制FASN 活性可以破坏脂肪酸的产生,并可能影响各种细胞过程。
- ¥ 678
规格
数量
TVB-3166
T171801533438-83-3
TVB-3166 是一种口服有效的,可逆和选择性脂肪酸合成酶 (FASN) 抑制剂,对于 FASN 和细胞棕榈酸酯合成的IC50分别为 42 nM 和 81 nM。它诱导细胞凋亡,抑制体内异种移植肿瘤生长。
- ¥ 348
规格
数量
L-Carnitine
T0846541-15-1
L-Carnitine (L(-)-Carnitine) 是一种人内源性分子,在人体内以蛋氨酸和赖氨酸为底物进行生物合成,并参与脂肪酸代谢。L-Carnitine 将长链脂肪酰辅酶A 转运到线粒体。L-Carnitine 能够改善许多先天性代谢错误的代谢失衡。
- ¥ 326
规格
数量
Desoxyrhaponticin
TJS038730197-14-9
Desoxyrhaponticin (Deoxyrhaponticin) 是来自西藏营养食品唐古特大黄中的一种二苯乙烯苷。它是脂肪酸合成酶抑制剂,抑制细胞内 FAS 活性,下调人乳腺癌 MCF-7细胞中 FAS 的表达。它是控制糖尿病餐后高血糖的潜在药物。
- ¥ 297
规格
数量
Dihydrocurcumin
T3S170176474-56-1
Dihydrocurcumin 是姜黄素的主要代谢物,具有减少脂肪积累和减少氧化应激反应的作用。Dihydrocurcumin 可调控SREBP-1C,PNPLA3 和 PPARα 的 mRNA 和蛋白表达水平,使pAKT 和 PI3K 的蛋白表达水平增高,通过 Nrf2 信号通路使细胞胞内 NO 和 ROS 的含量减少。
- ¥ 1280
规格
数量
Beta-Hydroxyisovalerylshikonin
TN14407415-78-3
Beta-hydroxyisovalerylshikonin 是分离自Lithospermium radix 的天然产物,具有抑制PTK 的作用, 对 EGFR 和 v-Src 受体作用的IC50分别为 0.7 μM 和 1 μM。它对多种肿瘤细胞系均有抑制作用,可以高效诱导 NCI-H522 和 DMS114 细胞的死亡。
- ¥ 1420
规格
数量
Isoscoparin
TN180320013-23-4
Isoscoparin 源自 Gentiana algida Pall,具有抗氧化和抗脂肪生成活性。Isoscoparin 可用于预防和治疗肥胖的研究。
- ¥ 570
规格
数量
Fatostatin hydrobromide
 客户已引用
客户已引用
T6832298197-04-3
Fatostatin hydrobromide (Fatostatin A HBr) 是一种 SREBP 活化的特异性抑制剂,可抑制 SREBP-1 和 SREBP-2 的活化。它与 SCAP (SREBP 裂解激活蛋白) 结合,抑制 SREBPs 的 ER-Golgi 易位。它具有抗肿瘤作用,能抑制 ob ob 小鼠的高血糖。它抑制了细胞中成脂基因的转录。
- ¥ 196
规格
数量
trans-C75
T10656191282-48-1
trans-C75 ((±)-C75) 是一种 C75 的对映异构体。其中 C75 是一种脂肪酸合成酶 (FASN) 的抑制剂。
- ¥ 377
规格
数量
Fatostatin 客户已引用
客户已引用
T9266125256-00-0
Fatostatin A 是一种SREBP 活化的特异性抑制剂,能够抑制 SREBP-1 和 SREBP-2 的活化。它与 SCAP (SREBP 裂解激活蛋白) 结合,抑制 SREBPs 的 ER-Golgi 易位。它具有抗肿瘤活性,能抑制ob ob 小鼠的高血糖。它抑制细胞中成脂基因的转录。
- ¥ 237
规格
数量
Lycorine 客户已引用
客户已引用
T3324476-28-8
Lycorine (Narcissine) 是从金眼科植物科中提取的一种天然生物碱。它是一种具有口服活性的SCAP 抑制剂,Kd 值 15.24 nM。它也是黑色素瘤血管生成抑制剂,有用于前列腺癌和代谢疾病的研究潜力。
- ¥ 251
规格
数量
UCM05
T218311094451-90-7
UCM05 (G28UCM) (G28UCM) 是一种有效的脂肪酸合酶 (FASN) 抑制剂,对 HER2+ 乳腺癌异种移植物具有作用活性,且在抗 HER2 耐药细胞系中具有活性。UCM05 是一种丝状温度敏感蛋白 Z (FtsZ) 抑制剂,可抑制革兰氏阳性菌B. subtilis 生长,MIC 值为 100 μM,但对革兰氏阴性菌E. coli 缺乏活性。
- ¥ 328
规格
数量
Pyrazinamide
T142698-96-4
Pyrazinamide (Pyrazinecarboxamide) 是一种口服抗结核类抗生素。它是一种前药,通过结核分枝杆菌pncA 基因编码的 PZase 烟酰胺酶转化为活性吡嗪酸形式。
- ¥ 326
规格
数量
Fasnall
T27307929978-58-5
Fasnall 是一种选择性 FASN 抑制剂,通过其辅因子结合位点起作用。 Fasnall 在 HER2(+) 乳腺癌的 MMTV-Neu 模型中显示出有效的抗肿瘤活性,尤其是与卡铂联合使用时。
- ¥ 378
规格
数量
Pedunculoside
T282442719-32-4
Pedunculoside 是从 Ilex rotunda Thunb 中提取的,通过对脂质形成和脂肪酸 β-氧化的调节而发挥降脂作用。
- ¥ 260
规格
数量
Pseudoprotodioscin
T5S0246102115-79-7
Pseudoprotodioscin 是一种呋喃葡糖苷,抑制SREBP1 2和microRNA 33a b 水平,降低胆固醇和甘油三酯合成相关的基因表达。
- ¥ 760
规格
数量
trans-Chalcone
T3322614-47-1
trans-Chalcone (Chalkone) 是从 Aronia melanocarpa 果皮中分离出来的一种天然产物,是类黄酮前体的双酚核心结构。它是脂肪酸合酶和 α-淀粉酶的抑制剂,具有抗真菌和抗癌活性。
- ¥ 247
规格
数量
Fasnall HCl
T27307L
Fasnall HCl 是一种FASN 选择性抑制剂,通过其辅助因子结合位点起作用。Fasnall HCl 在HER2(+)乳腺癌MMTV-Neu 模型中也显示出强大的抗肿瘤活性,特别是与卡铂联合使用时。
- ¥ 773
规格
数量
Trimetazidine dihydrochloride 客户已引用
客户已引用
T098813171-25-0
Trimetazidine dihydrochloride (Vastarel F) 是细胞保护性抗缺血剂,也用作缺血性心脏病或心绞痛的血管扩张剂,具有抗氧化,抗炎,抗伤害和胃保护作用。它可通过抑制脂肪酸代谢提高心肌葡萄糖利用率。
- ¥ 313
规格
数量
FT113
T79471630808-89-7
FT113 是口服具有活力的脂肪酸合酶抑制剂,对全长重组人 FASN 酶的 IC50=213 nM。在 BT474 细胞中,它抑制 FASN 的特性,IC50=90 nM。它具有抗增殖作用,在体内和体外实验中,都具有抗癌作用。
- ¥ 879
规格
数量
Fas C-Terminal Tripeptide Acetate
T21724L
Fas C-Terminal Tripeptide Acetate 显示出对 Fas FAP-1 结合的抑制活性。
- ¥ 397
规格
数量
BI 99179
T145701291779-76-4
BI 99179 是一种具有选择性和高效性的 I 型脂肪酸合成酶 (FAS) 抑制剂,是一种靶向 FAS 的工具化合物,可用于研究癌症。
- ¥ 347
规格
数量
Cerulenin
TQ026017397-89-6
Cerulenin 是广泛使用的天然脂肪酸合成酶抑制剂。它是由真菌Cephalosporium caeruleus 产生的。它抑制拓扑异构酶I 催化活性并增强 SN-38 诱导的细胞凋亡。它具有抗真菌和抗肿瘤活性。
- ¥ 750
规格
数量
Icariside E4
TN5431126253-42-7
Icariside E4是一种从小叶榆中提取得到天然化合物, 通过AMPK 磷酸化和抑制HepG1细胞中MID1IP2的低脂化作用。Icariside E4具有抗伤害,抗氧化,抗阿尔茨海默氏症和抗炎作用,抑制了SREBP-1c,肝脏X 受体-α(LXR)和FASN 在HepG2细胞中从头脂肪生成的表达。Icariside E4是治疗脂肪肝疾病的有效候选药物,在HepG1细胞中具有低脂化潜力。
- ¥ 10980
规格
数量
GSK2194069
T154291332331-08-4
GSK2194069 是 一种具有活性的脂肪酸合成酶 (FASN) 的 β-酮基还原酶 (KR)特异性抑制剂,在检测释放的 CoA 的试验中测的 IC50 为7.7 nM。GSK2194069 通过作用于乙酰乙酰辅酶 A 和 NADPH 来抑制 FAS 的癌细胞增殖。
- ¥ 1099
规格
数量
Hydroxycitric acid
TN17516205-14-7
(-)-Hydroxycitric acid (HCA) can inhibit fat synthesis and reduces food intake, the primary mechanism of action of HCA appears to be related to its ability to act as a competitive inhibitor of the enzyme ATP-citrate lyase, which catalyzes the conversion of citrate and coenzyme A to oxaloacetate and acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA), primary building blocks of fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis.
- ¥ 380
规格
数量
Albaspidin AP
TN136559092-91-0
Albaspidin-AP, -PP, -PB inhibit Fatty acid synthase (FAS) with IC50 values ranging from 23.1+ -1.4 to 71.7+ -3.9 microM, they could be considered to be a promising class of FAS inhibitors, and FAS is emerging as a potential therapeutic target to treat can
- ¥ 2470
规格
数量
FAS-IN-1 Tosylate
T11266L
FAS-IN-1 Tosylate is an effective fatty acid synthase inhibitor;Has an IC50 of 10 nM.
- ¥ 11700
规格
数量
1-Hydroxy-2-oxopomolic acid
TN2535217466-37-0
1β-Hydroxy-2-oxopomolic acid inhibits adipocyte differentiation through downregulation of various adipocytokines by blocking PPARγ and C EBPα expression.
- ¥ 4420
规格
数量
转到第1页
/ 1 页