 您的购物车当前为空
您的购物车当前为空
Forskolin
一键复制产品信息别名 毛喉素, FSK, Colforsin, Coleonol
Forskolin (Coleonol) 属于天然产物,是一种腺苷酸环化酶激活剂 (EC50=0.5 μM)。Forskolin 可以增加 cAMP 水平,可以激活 PXR 和 FXR,也可以诱导细胞自噬。Forskolin 对心脏产生正性肌力作用,具有血小板抗凝集和降压作用。

为众多的药物研发团队赋能,
让新药发现更简单!
Forskolin
一键复制产品信息Forskolin (Coleonol) 属于天然产物,是一种腺苷酸环化酶激活剂 (EC50=0.5 μM)。Forskolin 可以增加 cAMP 水平,可以激活 PXR 和 FXR,也可以诱导细胞自噬。Forskolin 对心脏产生正性肌力作用,具有血小板抗凝集和降压作用。
| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | ¥ 218 | 现货 | |
| 5 mg | ¥ 496 | 现货 | |
| 10 mg | ¥ 668 | 现货 | |
| 25 mg | ¥ 949 | 现货 | |
| 50 mg | ¥ 1,230 | 现货 | |
| 100 mg | ¥ 1,960 | 现货 | |
| 200 mg | ¥ 3,150 | 现货 | |
| 500 mg | ¥ 4,970 | 现货 | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | ¥ 546 | 现货 |
产品介绍
| 产品描述 | Forskolin (Coleonol) is a natural product, an adenylate cyclase activator (EC50=0.5 μM). Forskolin increases cAMP levels, activates PXR and FXR, and induces autophagy. Forskolin produces positive inotropic effects in the heart, and has platelet anticoagulant and antihypertensive effects. |
| 靶点活性 | MCF-7 cells:63.3 μM, Adenylyl cyclase:0.5 μM (cell free), adenylyl cyclase (type I):0.5 μM (EC50) |
| 体外活性 | 方法:大鼠肾上腺髓质嗜铬瘤细胞 PC12 用 Forskolin (0.01-10 µM) 处理 3-48 h,使用 MTT 方法检测细胞生长抑制情况。 |
| 体内活性 | 方法:为检测体内抗肿瘤活性,将 Forskolin (4-5 mg/kg in PBS/DMSO solution (15:1)) 腹腔注射给携带鼠多发性骨髓瘤肿瘤 MOPC315 的 BALB/c nude 小鼠,在肿瘤细胞注射后的第 2/4/6 天给药。 |
| 激酶实验 | For Jak3 kinase assays, Fsk-treated MT-2 cells were lysed, clarified, and immunoprecipitated using Jak3 antibody as described above. Kinase reactions were carried out as described previously at 30 °C for 20 min. For PKA kinase assays, untreated MT-2 cells were lysed, and Jak3 was immunoprecipitated and bound to PAS beads as described previously. Immunoprecipitated Jak3 was washed with kinase buffer (50 mM Hepes-NaOH (pH 7.4), 10 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM EGTA, 0.5 mM DTT, 20 μg/ml aprotinin, 10 μg/ml leupeptin, 1 μg/ml pepstatin A) and incubated with 200 μM ATP and purified protein kinase A catalytic subunit (PKAc) as indicated in the figure legends. Kinase reactions were carried out at 32 °C for 30 min followed by vigorous washing of the beads with cold kinase wash buffer as described previously. For [γ-32P]ATP radiolabeled kinase assays using recombinant Jak3, Hek293 cells were transfected with wild type (WT) Jak3 or kinase-dead Jak3 K855A using Lipofectamine 2000 according to the manufacturer's instructions. Cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated with Jak3 antibody. Jak3-bound PAS beads were washed three times in cold lysis buffer followed by kinase buffer. Kinase reactions were initiated by adding 10 μCi [γ-32P]ATP, 10 μm unlabeled ATP, and 1 μg of purified PKAc to Jak3-bound PAS bead reaction mixtures. Kinase reactions were performed at 32 °C for 30 min. Jak3-bound PAS beads were washed three times in radioimmunoassay buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 75 mM NaCl, 20 mM EDTA, 10 mM EGTA, 20 mM Na4P2O7, 50 mM NaF, 20 mM 2-glycerolphosphate, 1 mM p-nitrophenyl phosphate, 0.1% Triton X-100) and one time in kinase wash buffer. The reactions were stopped by adding 2× SDS-PAGE sample buffer followed by SDS-PAGE. Coomassie stainable Jak3 bands were excised from the PVDF membrane and subjected to phosphoamino acid analysis [2]. |
| 细胞实验 | Kit 225 or MT-2 cells were treated with 1, 5, 10, 20, 50, or 100 μM Forskolin for 20 min at 37 °C. Cells were lysed and clarified by centrifugation, and the concentration of cAMP was detected by direct cAMP ELISA. Optical density was measured at 405 nm, and the concentration of intracellular cAMP was calculated using a weighted four parameter logistic curve according to the manufactures instructions [2]. |
| 动物实验 | Forskolin was dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and injected intraperitoneally into neonatal mice at postnatal days 4 (P4) and 5 (P5). Mice injected with DMSO served as the controls. The treated mice were euthanized at P6, and their retinas were isolated for whole-mount immunohistochemistry (IHC). We first tested the effect of different concentrations of forskolin on the survival rate and retinal vasculature and determined the optimal concentration, 1.0 μg/50 μL (0.3 mg/kg) at P4 and 1.5 μg/50 μL (0.5 mg/kg) at P5, used to compare the retinal vascular phenotypes between WT mice and Mrp4-deficient mice [4]. . After acclimatization for 2 weeks, animals were randomly divided into four groups of eight rats each and treated for six consecutive weeks as follows: The first group was treated with CCl4 (50% CCl4/corn oil; 0.5 mL·kg?1, i.p.) twice a week to induce liver fibrosis. The second group was given forskolin only at a dose of 10 mg·kg?1, i.p., dissolved in a DMSO/saline solution (1:49) five times a week. The third group was given both CCl4 and forskolin. The dose of forskolin used here was based on the results of our preliminary study. The fourth group served as the normal control, receiving vehicles only. At 24 h after the last injection, blood samples were collected from the retro‐orbital plexus after light anesthesia with sodium pentobarbital (50 mg·kg?1, i.p.). Serum was separated by centrifugation at 3000× g for 10 min and was used for the assessment of liver functions. Rats were killed by cervical dislocation, and livers were removed and weighed. A portion of liver tissue was washed and homogenized to obtain a 20% (w·v?1) homogenate, which was used for assessment of oxidative stress, inflammatory and fibrogenic markers. Another portion was placed in formalin for immunohistochemical and histopathological analyses. The remainder was stored at ?80°C, together with the 20% homogenate, until needed [5]. |
| 别名 | 毛喉素, FSK, Colforsin, Coleonol |
| 分子量 | 410.50 |
| 分子式 | C22H34O7 |
| CAS No. | 66575-29-9 |
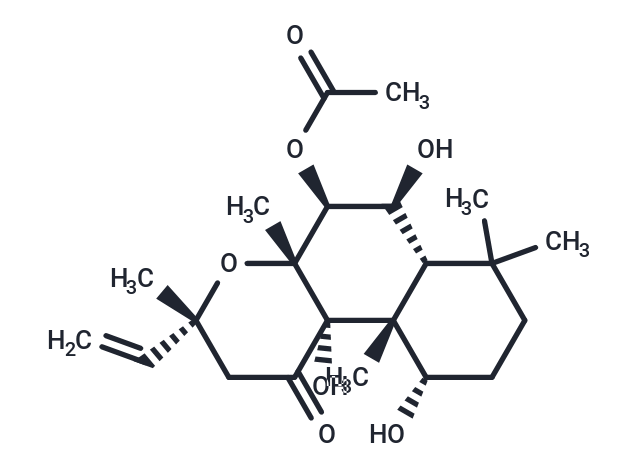
| Smiles | CC(=O)O[C@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@@H]2C(C)(C)CC[C@H](O)[C@]2(C)[C@@]2(O)C(=O)C[C@@](C)(O[C@]12C)C=C |
| 密度 | 1.23 g/cm3 |
| 颜色 | White |
| 物理性状 | Solid |
| 存储 | keep away from direct sunlight,keep away from moisture,store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 溶解度信息 | H2O: Insoluble DMSO: 245.00 mg/mL (596.83 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 15.00 mg/mL (36.54 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 体内实验配方 | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 3.00 mg/mL (7.31 mM), Solution. 请按顺序添加溶剂,在添加下一种溶剂之前,尽可能使溶液澄清。如有必要,可通过加热、超声、涡旋处理进行溶解。工作液建议现配现用。以上配方仅供参考,体内配方并不是绝对的,请根据不同情况进行调整。 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
溶液配制表 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 化合物与蛋白结合的复合物
化合物与蛋白结合的复合物
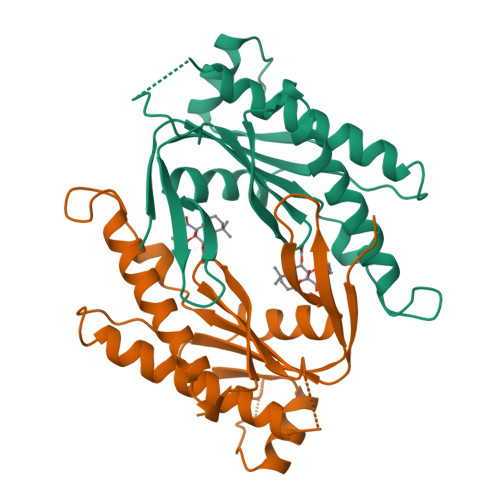
RAT TYPE II ADENYLYL CYCLASE C2 DOMAIN/FORSKOLIN COMPLEX
计算器
体内实验配液计算器
以上为“体内实验配液计算器”的使用方法举例,并不是具体某个化合物的推荐配制方式,请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解方案。
剂量转换
对于不同动物的给药剂量换算,您也可以参考 更多




 很棒
很棒
 |
|