购物车
 您的购物车当前为空
您的购物车当前为空
别名 甲胺盐酸盐
Methylamine HCl(甲胺盐酸盐)是Methylamine的盐形式。Methylamine暴露可通过激活NF-κB信号风险,引起活性氧的产生和细胞因子的产生,从而引起人类呼吸道细胞炎症和高血压。
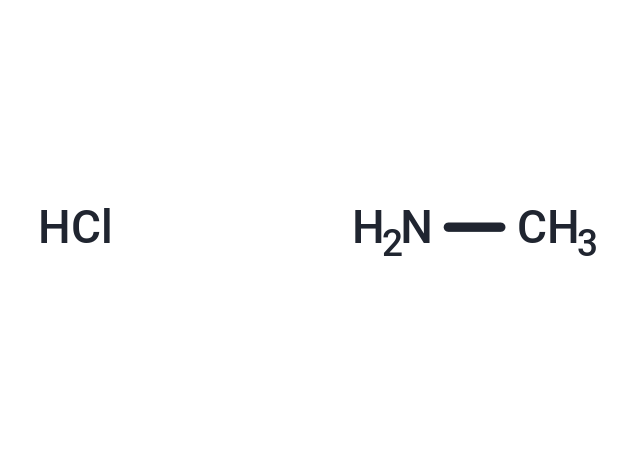
Methylamine HCl(甲胺盐酸盐)是Methylamine的盐形式。Methylamine暴露可通过激活NF-κB信号风险,引起活性氧的产生和细胞因子的产生,从而引起人类呼吸道细胞炎症和高血压。
| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | ¥ 168 | 现货 | |
| 100 mg | ¥ 252 | 现货 | |
| 500 mg | ¥ 554 | 现货 | |
| 1 g | ¥ 830 | 现货 |
| 产品描述 | Methylamine HCl is the salt form of Methylamine. Methylamine exposure can cause inflammation and hypertension in human respiratory cells by activating NF-B signaling risk, causing reactive oxygen species production and cytokine production. |
| 别名 | 甲胺盐酸盐 |
| 分子量 | 67.52 |
| 分子式 | CH6ClN |
| CAS No. | 593-51-1 |
| Smiles | Cl.CN |
| 密度 | 0.489 g/cm3. Temperature:26.6 °C.;0.528 g/cm3. Temperature:29.6 °C. |
| 存储 | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
对于不同动物的给药剂量换算,您也可以参考 更多