 您的购物车当前为空
您的购物车当前为空
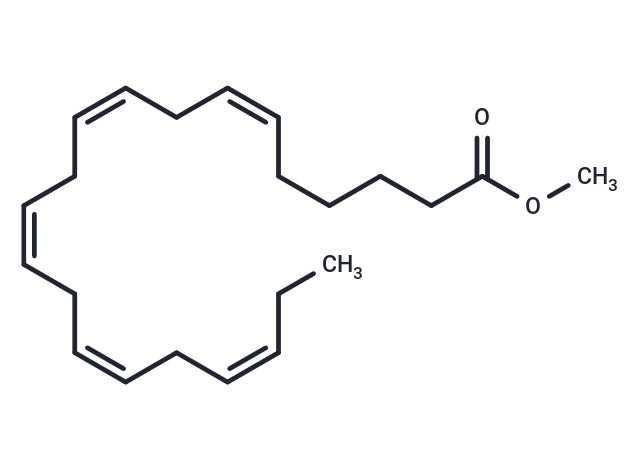
Heneicosapentaenoic Acid methyl ester
一键复制产品信息别名 HPA methyl ester
Heneicosapentaenoic Acid (HPA) is a fatty acid found in small amounts in Bryopsis pennata Lamouroux green algae and fish oils, with a structure similar to eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), but with an additional carbon at the carboxyl end, resulting in the first double bond being in the Δ6 position. HPA is important for researching the impact of double bond positions in n-3 fatty acids, as it integrates into phospholipids and triacylglycerol in vivo as effectively as EPA and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), while strongly inhibiting the synthesis of arachidonic acid from linoleic acid. Despite being a poor substrate for prostaglandin H (PGH) synthase and 5-lipoxygenase, HPA can rapidly deactivate PGH synthase. HPA methyl ester, in certain formulations, acts as a prodrug to enhance cellular uptake of HPA before being converted into free acid by esterases, and serves as a useful reference standard.
Heneicosapentaenoic Acid methyl ester
一键复制产品信息Heneicosapentaenoic Acid (HPA) is a fatty acid found in small amounts in Bryopsis pennata Lamouroux green algae and fish oils, with a structure similar to eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), but with an additional carbon at the carboxyl end, resulting in the first double bond being in the Δ6 position. HPA is important for researching the impact of double bond positions in n-3 fatty acids, as it integrates into phospholipids and triacylglycerol in vivo as effectively as EPA and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), while strongly inhibiting the synthesis of arachidonic acid from linoleic acid. Despite being a poor substrate for prostaglandin H (PGH) synthase and 5-lipoxygenase, HPA can rapidly deactivate PGH synthase. HPA methyl ester, in certain formulations, acts as a prodrug to enhance cellular uptake of HPA before being converted into free acid by esterases, and serves as a useful reference standard.
| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg | 待询 | 8-10周 | |
| 50 mg | 待询 | 8-10周 |
产品介绍
| 产品描述 | Heneicosapentaenoic Acid (HPA) is a fatty acid found in small amounts in Bryopsis pennata Lamouroux green algae and fish oils, with a structure similar to eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), but with an additional carbon at the carboxyl end, resulting in the first double bond being in the Δ6 position. HPA is important for researching the impact of double bond positions in n-3 fatty acids, as it integrates into phospholipids and triacylglycerol in vivo as effectively as EPA and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), while strongly inhibiting the synthesis of arachidonic acid from linoleic acid. Despite being a poor substrate for prostaglandin H (PGH) synthase and 5-lipoxygenase, HPA can rapidly deactivate PGH synthase. HPA methyl ester, in certain formulations, acts as a prodrug to enhance cellular uptake of HPA before being converted into free acid by esterases, and serves as a useful reference standard. |
| 别名 | HPA methyl ester |
| 分子量 | 330.5 |
| 分子式 | C22H34O2 |
| CAS No. | 65919-53-1 |
| 存储 | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
计算器
体内实验配液计算器
以上为“体内实验配液计算器”的使用方法举例,并不是具体某个化合物的推荐配制方式,请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解方案。
剂量转换
对于不同动物的给药剂量换算,您也可以参考 更多





 还可以
还可以
 |
|