- 全部删除
 您的购物车当前为空
您的购物车当前为空
购物车
Angiopoietin 家族 (Angiopoietin)
(64)
Ephrin 家族 (Ephrin Family)
(53)
Insulin-like 生长因子家族 (Insulin-like Growth Factors, IGFs)
(53)
神经营养因子家族 (Neurotrophins)
(108)
纤维生长因子家族 (Fibroblast Growth Factors, FGFs)
(56)
血小板源生长因子 (Platelet-Derived Growth Factors, PDGFs)
(21)
血管内皮生长因子家族 (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors, VEGFs)
(40)
表皮生长因子家族 (Epidermal Growth Factor Family, EGFs)
(50)
转化生长因子-β 家族 (Transforming Growth Factor-β family, TGF-βs)
(94)
骨形成蛋白家族 (Bone Morphogenetic Proteins, BMPs)
(22)
纤维生长因子家族 (Fibroblast Growth Factors, FGFs)
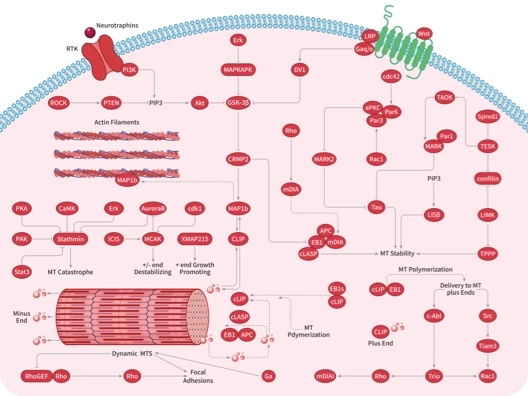
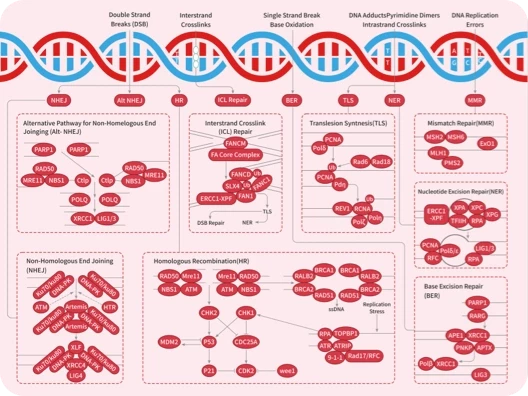
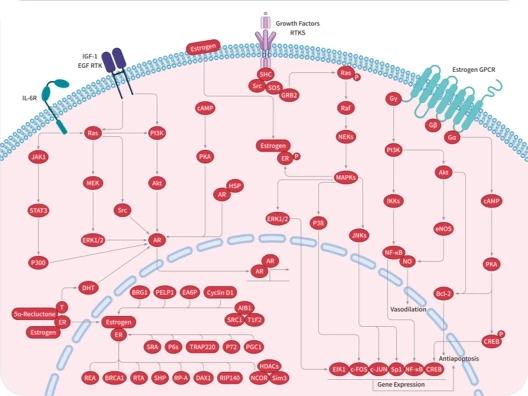
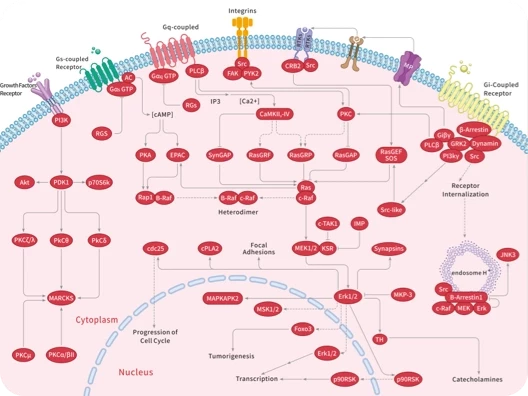
纤维细胞生长因子 (Fibroblast Growth Factors, FGFs) 是由巨噬细胞产生的细胞信号蛋白家族,它们参与多种过程,最显着的是作为动物细胞正常发育的关键元素。其功能的任何不规则都会导致一系列发育缺陷。FGF通常作为细胞外来源的全身或局部循环分子,激活细胞表面受体。FGF是具有多种作用的多功能蛋白,它们最常见的是有丝分裂原,但也具有调节、形态学和内分泌作用。FGF的一个决定性特性是它们与肝素和硫酸乙酰肝素结合。
FGF-10 Protein, Human, Recombinant
TMPY-01061
Fibroblast growth factor 10 (FGF10) is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and are involved in a variety of biological processes, including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. FGF10 exhibits mitogenic activity for keratinizing epidermal cells, but essentially no activity for fibroblasts, which is similar to the biological activity of FGF7. FGF10 plays an important role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation and cell differentiation. FGF10 is required for normal branching morphogenesis. It may play a role in wound healing. Defects in FGF10 are the cause of autosomal dominant aplasia of lacrimal and salivary glands (ALSG). ALSG has variable expressivity, and affected individuals may have aplasia or hypoplasia of the lacrimal, parotid, submandibular and sublingual glands and absence of the lacrimal puncta. The disorder is characterized by irritable eyes, recurrent eye infections, epiphora (constant tearing) and xerostomia (dryness of the mouth), which increases the risk of dental erosion, dental caries, periodontal disease and oral infections.
- ¥ 1650
规格
数量
FGF-2 Protein, Human, Recombinant
TMPY-00749
FGF-2 Protein, Human, Recombinant is expressed in E. coli expression system. The predicted molecular weight is 16.5 kDa and the accession number is P09038-4.
- ¥ 560
规格
数量
FGF-8b Protein, Human, Recombinant
TMPY-06986
In mammalian embryos, transient Fgf8 expression defines the developing isthmic region, lying between the midbrain and the first rhombomere, but there has been uncertainty about the existence of a distinct isthmic segment in postnatal mammals. Retinoic acid (RA) directly represses Fgf8 through a RARE-mediated mechanism that promotes repressive chromatin, thus providing valuable insight into the mechanism of RA-FGF antagonism during progenitor cell differentiation. Fgf8 encodes a key signaling factor, and its precise regulation is essential for embryo patterning.
- ¥ 2940
规格
数量
FGF-7/KGF Protein, Human, Recombinant (His)
TMPY-00403
FGF-7 KGF Protein, Human, Recombinant (His) is expressed in E. coli expression system with His tag. The predicted molecular weight is 21 kDa and the accession number is P21781.
- ¥ 1050
规格
数量
FGF-9 Protein, Human, Recombinant
TMPJ-00090
Fibroblast Growth Factor 9 (FGF-9) belongs to the Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and are involved in a variety of biological processes, including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. FGF-9 plays an important role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, cell differentiation and cell migration. In addition, FGF-9 may have a role in glial cell growth and differentiation during development, gliosis during repair and regeneration of brain tissue after damage, differentiation and survival of neuronal cells, and growth stimulation of glial tumors.
- ¥ 910
规格
数量
FGF-2 Protein, Mouse, Recombinant
TMPJ-00037
FGF basic is one of 22 mitogenic proteins of the FGF family, which show 35-60% amino acid conservation. Unlike other FGFs, FGF acidic and basic lack signal peptides and are secreted by an alternate pathway. The 17 kDa mouse sequence has 98% aa identity with rat, and 95% identity with human, bovine, and sheep FGF basic. Binding of FGF to heparin or cell surface HSPG is necessary for binding, dimerization and activation of tyrosine kinase FGF receptors. FGF basic binds other proteins, polysaccharides and lipids with lower affinity. Expression of FGF basic is nearly ubiquitous but disruption of the mouse FGF basic gene gives a relatively mild phenotype, suggesting compensation by other FGF family members. FGF basic modulates such normal processes as angiogenesis, wound healing and tissue repair, embryonic development and differentiation, neuronal function and neural degeneration. Transgenic overexpression of FGF basic results in excessive proliferation and angiogenesis is reminiscent of a variety of pathological conditions.
- ¥ 380
规格
数量
FGF-4 Protein, Human, Recombinant
TMPY-05004
FGF (fibroblast growth factor) signalling is known to be required for many aspects of mesoderm formation and patterning during Xenopus development and has been implicated in regulating genes required for the specification of both blood and skeletal muscle lineages. Fibroblast growth factor 4 (FGF4) signaling induces differentiation from embryonic stem cells (ESCs) via the phosphorylation of downstream molecules such as mitogen-activated protein kinase extracellular signal-related kinase (MEK) and extracellular signal-related kinase 1 2 (ERK1 2). Fibroblast Growth Factor 4 (FGF-4) could not only increase the proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs), but also induce BMSCs into hepatocyte-like cells in vitro. FGF4 transduced BMSCs contributed to liver regeneration might by the transplanted microenvironment. The FGF4-bFGF BMSCs thus can enhance the survival of the transplanted cells, diminish myocardial fibrosis, promote myocardial angiogenesis, and improve cardiac functions.
- ¥ 875
规格
数量
FGF-17 Protein, Human, Recombinant
TMPY-03104
FGF-13, also known as FGF17, belongs to the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. Members of this family show broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and play a role in a variety of biological processes including embryonic development cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. FGF-13 is preferentially expressed in the embryonic brain. It interacts with FGFR3 and FGFR4. FGF-13 plays an important role in the regulation of embryonic development and as signaling molecule in the induction and patterning of the embryonic brain. It is also required for normal brain development.
- ¥ 1050
规格
数量
FGF-9 Protein, Mouse, Recombinant (His)
TMPJ-01011
Fibroblast growth factor-9 (FGF-9) is an approximately 26 kDa secreted glycoprotein of the FGF family. Secreted mouse FGF-9 lacks the N-terminal 1-3 aa and shares >98% sequence identity with rat, human, equine, porcine and bovine FGF-9. FGF-9 plays an important role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, cell differentiation and cell migration. In the mouse embryo the location and timing of FGF-9 expression affects development of the skeleton, cerebellum, lungs, heart, vasculature, digestive tract, and testes .It may have a role in glial cell growth and differentiation during development, gliosis during repair and regeneration of brain tissue after damage, differentiation and survival of neuronal cells, and growth stimulation of glial tumors. Deletion of mouse FGF-9 is lethal at birth due to lung hypoplasia, and causes rhizomelia, or shortening of the proximal skeleton. An unusual constitutive dimerization of FGF 9 buries receptor interaction sites which lowers its activity, and increases heparin affinity which inhibits diffusion. A spontaneous mouse mutant, Eks, interferes with dimerization, resulting monomeric, diffusible FGF-9 that causes elbow and knee synostoses (joint fusions) due to FGF-9 misexpression in developing joints.
- ¥ 810
规格
数量
FGF-18 Protein, Mouse, Recombinant (His)
TMPY-01415
FGF-18 Protein, Mouse, Recombinant (His) is expressed in HEK293 mammalian cells with His tag. The predicted molecular weight is 22.5 kDa and the accession number is A0A7U3JW51.
- ¥ 2940
规格
数量
FGF-1 Protein, Human, Recombinant
TMPY-00756
FGF-1 Protein, Human, Recombinant is expressed in E. coli expression system. The predicted molecular weight is 16 kDa and the accession number is P05230-1.
- ¥ 560
规格
数量
FGF-21 Protein, Human, Recombinant (Low Endotoxin)
TMPY-06935
FGF-21 Protein, Human, Recombinant is expressed in E. coli expression system. The predicted molecular weight is 19.55 kDa and the accession number is NP_061986.1.
- ¥ 2430
规格
数量
FGF-21 Protein, Mouse, Recombinant (His)
TMPY-02139
FGF-21 Protein, Mouse, Recombinant (His) is expressed in HEK293 mammalian cells with His tag. The predicted molecular weight is 21.3 kDa and the accession number is Q9JJN1.
- ¥ 1950
规格
数量
FGF-2 Protein, Chicken, Recombinant (His)
TMPH-00368
Acts as a ligand for FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3 and FGFR4. Also acts as an integrin ligand which is required for FGF2 signaling. Plays an important role in the regulation of cell survival, cell division, cell differentiation and cell migration. Functions as a potent mitogen in vitro. Can induce angiogenesis. FGF-2 Protein, Chicken, Recombinant (His) is expressed in yeast with N-6xHis tag. The predicted molecular weight is 18.3 kDa and the accession number is P48800.
- ¥ 1620
规格
数量
FGF-1 Protein, Mouse, Rat, Recombinant
TMPY-01089
FGF-1 Protein, Mouse, Rat, Recombinant is expressed in E. coli expression system. The predicted molecular weight is 16 kDa and the accession number is P61148.
- ¥ 560
规格
数量
FGF-7/KGF Protein, Human, Recombinant
TMPJ-00073
Fibroblast growth factor 7 (FGF7) is a secreted protein which is mainly located in epithelial cells and belongs to the heparin-binding growth factors family. FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and are involved in a variety of biological processes, including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. FGF7 is a potent epithelial cell-specific growth factor, whose mitogenic activity is predominantly exhibited in keratinocytes but not in fibroblasts and endothelial cells. It is possible major paracrine effector of normal epithelial cell proliferation.
- ¥ 1170
规格
数量
FGF-2 Protein, Human, Recombinant (K128N)
TMPJ-00039
FGF-2 Protein, Human, Recombinant (K128N) is expressed in E. coli expression system. The predicted molecular weight is 17 KDa and the accession number is P09038-2.
- ¥ 540
规格
数量
FGF-9 Protein, Human, Recombinant (hFc)
TMPY-00804
FGF-9 Protein, Human, Recombinant (hFc) is expressed in HEK293 mammalian cells with hFc tag. The predicted molecular weight is 54 and 37 kDa and the accession number is A0A7U3L6D0.
- ¥ 1350
规格
数量
FGF-8a Protein, Human, Recombinant
TMPY-00005
In mammalian embryos, transient Fgf8 expression defines the developing isthmic region, lying between the midbrain and the first rhombomere, but there has been uncertainty about the existence of a distinct isthmic segment in postnatal mammals. Retinoic acid (RA) directly represses Fgf8 through a RARE-mediated mechanism that promotes repressive chromatin, thus providing valuable insight into the mechanism of RA-FGF antagonism during progenitor cell differentiation. Fgf8 encodes a key signaling factor, and its precise regulation is essential for embryo patterning.
- ¥ 2930
规格
数量
FGF-2 Protein, Mouse, Recombinant (His)
TMPY-00210
FGF-2 Protein, Mouse, Recombinant (His) is expressed in E. coli expression system with His tag. The predicted molecular weight is 18.5 kDa and the accession number is P15655.
- ¥ 2430
规格
数量
FGF-19 Protein, Human, Recombinant
TMPY-02907
FGF19, also known as FGF-19, is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and are involved in a variety of biological processes, including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. FGF19 interacts with FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3 and FGFR4. Affinity between fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) and their receptors is increased by KL, KLB and heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycans that function as coreceptors. It interacts with KL and KLB directly. However, it interacts with FGFR4 in the presence of heparin, KL or KLB. FGF19 is involved in the suppression of bile acid biosynthesis through down-regulation of CYP7A1 expression, following positive regulation of the JNK and ERK1 2 cascades. It also stimulates glucose uptake in adipocytes.
- ¥ 1950
规格
数量
FGF-2 Protein, Rat, Recombinant
TMPJ-00842
FGF-basic is a members of the Fibroblast Growth Factors (FGFs) family. The family constitutes a large family of proteins involved in many aspects of development including cell proliferation, growth, and differentiation. They act on several cell types to regulate diverse physiologic functions including angiogenesis, cell growth, pattern formation, embryonic development, metabolic regulation, cell migration, neurotrophic effects, and tissue repair. FGF-basic is a non-glycosylated heparin binding growth factor that is expressed in the brain, pituitary, kidney, retina, bone, testis, adrenal gland liver, monocytes, epithelial cells and endothelial cells. FGF-basic signals through FGFR 1b, 1c, 2c, 3c and 4.
- ¥ 570
规格
数量
FGF-4 Protein, Mouse, Recombinant
TMPJ-00835
Fibroblast growth factor 4(FGF-4) is a heparin binding member of the FGF family. The human FGF4 cDNA encodes 206 amino acids (aa) with a 33 aa signal sequence and a 173 aa mature protein with an FGF homology domain that contains a heparin binding region near the C-terminus. Mature human FGF4 shares 91%, 82%, 94% and 91% aa identity with mouse, rat, canine and bovine FGF4, respectively. Human FGF-4 has been shown to exhibit cross species activity. Expression of FGF-4 and its receptors, FGF R1c, 2c, 3c and 4, is spatially and temporally regulated during embryonic development. FGF-4 is proposed to play a physiologically relevant role in human embryonic stem cell selfrenewal. It promotes stem cell proliferation, but may also aid differentiation depending on context and concentration, and is often included in embryonic stem cell media in vitro. FGF-4 is mitogenic for fibroblasts and endothelial cells in vitro and has autocrine transforming potential. It is a potent angiogenesis promoter in vivo and has been investigated as therapy for coronary artery disease.
- ¥ 610
规格
数量
FGF-21 Protein, Cynomolgus, Recombinant (His)
TMPJ-01459
Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 (FGF21) is a growth factor that belongs to the FGF family. FGF family proteins play a central role during prenatal development and postnatal growth and regeneration of mamy tissues, by promoting cellular proliferation and differentiation. FGF21 is a potent activator of glucose uptake on adipocytes, protects animal from diet-induced obesity when overexpression in transgenic mice, and lower blood glucose and triglyceride levels when therapeutically adiministered to diabetic redents. FGF21 is produced by hepatocytes in reponse to free fatty acid stimulation of a PPARa RXR dimeric complex. This situation occurs clinically during starvation, or following the ingestionof a highly-fat low-carbohydrate diet. Upon FGF21 secretion, white adipose tissue is induced to release free fatty acids from triglyceride stores. Once free fatty acid reach hepatocytes, they are oxidized and reduced to acetyl-CoA. The acetyl-CoA is recombined into 4-carbon ketone bodies, release, and transported to peripheral tissue for TCA processing and energy generation.
- ¥ 820
规格
数量
FGF-17 Protein, Human, Recombinant (His)
TMPJ-00096
Fibroblast Growth Factor 17 (FGF17) is a member of the heparin-binding growth factors family that is prominently expressed in the cerebellum and cortex. Proteins of this family possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities and they are involved in a variety of biological processes including embryonic development cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth, and invasion. FGF17 plays an important role in the regulation of embryonic development and it acts as signaling molecule in the induction and patterning of the embryonic brain. In addition, FGF17 stimulates the proliferation and activation of cells that express FGF receptors.
- ¥ 820
规格
数量
FGF-14 Protein, Canine, Recombinant
TMPY-04033
FGF-14 Protein, Canine, Recombinant is expressed in E. coli expression system. The predicted molecular weight is 21.1 kDa and the accession number is XP_003363267.1.
- ¥ 2940
规格
数量
FGF-21 Protein, Human, Recombinant (mFc & Avi), Biotinylated
TMPK-00098
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is a peptide hormone that is synthesized by several organs and regulates energy homeostasis. Excitement surrounding this relatively recently identified hormone is based on the documented metabolic beneficial effects of FGF21, which include weight loss and improved glycemia. FGF-21 Protein, Human, Recombinant (mFc & Avi), Biotinylated is expressed in HEK293 mammalian cells with N-mFc-Avi tag. The predicted molecular weight is 46.9 kDa and the accession number is Q9NSA1.
- ¥ 5180
规格
数量
FGF-1 Protein, Canine, Recombinant
TMPY-03622
FGF-1 Protein, Canine, Recombinant is expressed in E. coli expression system. The predicted molecular weight is 16 kDa and the accession number is A0A8C0QGP1.
- ¥ 1950
规格
数量
FGF-20 Protein, Mouse, Recombinant
TMPH-02653
Neurotrophic factor that regulates central nervous development and function. FGF-20 Protein, Mouse, Recombinant is expressed in E. coli expression system. The predicted molecular weight is 23.6 kDa and the accession number is Q9ESL9.
- ¥ 3280
规格
数量
KSP37/FGFBP2 Protein, Human, Recombinant (His)
TMPY-05473
KSP37 FGFBP2 Protein, Human, Recombinant (His) is expressed in Baculovirus insect cells with His tag. The predicted molecular weight is 22.6 kDa and the accession number is Q9BYJ0.
- ¥ 3430
规格
数量
FGF-18 Protein, Human, Recombinant (His)
TMPY-02626
FGF-18 Protein, Human, Recombinant (His) is expressed in HEK293 mammalian cells with His tag. The predicted molecular weight is 22.3 kDa and the accession number is O76093.
- ¥ 1950
规格
数量
FGF-2 Protein, Human,Recombinant (Q65I, C96S, N111G)
TMPJ-00040
FGF-2 Protein, Human,Recombinant (Q65I, C96S, N111G) is expressed in E. coli expression system. The predicted molecular weight is 16 KDa and the accession number is P09038-2.
- ¥ 540
规格
数量
FGF-21 Protein, Hamster, Recombinant (His)
TMPY-05794
FGF-21 Protein, Hamster, Recombinant (His) is expressed in HEK293 mammalian cells with His tag. The predicted molecular weight is 21.16 kDa and the accession number is A0A1U7RD97.
- ¥ 3430
规格
数量
FGF-12 Protein, Human, Recombinant
TMPJ-01041
Fibroblast Growth Factor 12 (FGF-12) is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF-12 is probably involved in nervous system development and function. FGF-12 lacks the N-terminal signal sequence present in most of the FGF family members, but it contains clusters of basic residues that have been demonstrated to act as a nuclear localization signal. When transfectedinto mammalian cells, this protein accumulated in the nucleus, but was not secreted. The specific function of this gene has not yet been determined. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been reported.
- ¥ 620
规格
数量
FGF-19 Protein, Human, Recombinant (His)
TMPJ-00715
Fibroblast growth factor 19 (FGF19) is a secreted protein which belongs to the FGFs family. FGF19 is expressed in fetal brain, cartilage, retina, and adult gall bladder. FGFs modulate cellular activity via at least 5 distinct subfamilies of high-affinity FGF receptors (FGFRs): FGFR-1, -2, -3, and -4, all with intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity. FGFRs can be important for regulation of glucose and lipid homeostasis. FGF19 has important roles as a hormone produced in the ileum in response to bile acid absorption. It has been shown to cause resistance to diet-induced obesity and insulin desensitization and to improve insulin, glucose, and lipid profiles in diabetic rodents. FGF19 can be considered as a regulator of energy expenditure.
- ¥ 820
规格
数量
FGF-5 Protein, Mouse, Recombinant (His)
TMPH-02654
Plays an important role in the regulation of cell proliferation and cell differentiation. Required for normal regulation of the hair growth cycle. Functions as an inhibitor of hair elongation by promoting progression from anagen, the growth phase of the hair follicle, into catagen the apoptosis-induced regression phase. FGF-5 Protein, Mouse, Recombinant (His) is expressed in E. coli expression system with N-6xHis tag. The predicted molecular weight is 32.8 kDa and the accession number is P15656.
- ¥ 2290
规格
数量
FGF-6 Protein, Human, Recombinant
TMPY-03382
FGF6, also known as FGF-6, belongs to the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. Members of this family possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and are involved in a variety of biological processes, including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. FGF6 plays an important role in the regulation of cell proliferation, cell differentiation, angiogenesis and myogenesis. It is also required for normal muscle regeneration. FGF6 gene displayed oncogenic transforming activity when transfected into mammalian cells.
- ¥ 1050
规格
数量
FGF-10 Protein (Primary Amine Labeling), Human, Recombinant, Biotinylated
TMPK-00096
Fibroblast growth factor 10 (FGF10) regulates multiple stages of structural lung morphogenesis, cellular differentiation, and the response to injury. As a driver of lung airway branching morphogenesis, FGF10 signaling defects during development lead to neonatal lung disease. Lung diseases impact patients across the lifespan, from infants in the first minutes of life through the aged population. Congenital abnormalities of lung structure can cause lung disease at birth or make adults more susceptible to chronic disease.
- ¥ 5180
规格
数量
FGFb Protein, Rabbit, Recombinant (His & SUMO)
TMPH-03203
Acts as a ligand for FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3 and FGFR4. Also acts as an integrin ligand which is required for FGF2 signaling. Binds to integrin ITGAV:ITGB3. Plays an important role in the regulation of cell survival, cell division, cell differentiation and cell migration. Functions as a potent mitogen in vitro. Can induce angiogenesis. Mediates phosphorylation of ERK1 2 and thereby promotes retinal lens fiber differentiation. FGFb Protein, Rabbit, Recombinant (His & SUMO) is expressed in E. coli expression system with N-6xHis-SUMO tag. The predicted molecular weight is 28.4 kDa and the accession number is P48799.
- ¥ 1510
规格
数量
FGF-7/KGF Protein, Mouse, Recombinant (His)
TMPY-04206
FGF-7 KGF Protein, Mouse, Recombinant (His) is expressed in E. coli expression system with His tag. The predicted molecular weight is 21 kDa and the accession number is P36363.
- ¥ 2940
规格
数量
FGF-21 Protein, Human, Recombinant (His)
TMPY-01889
FGF-21 Protein, Human, Recombinant (His) is expressed in E. coli expression system with His tag. The predicted molecular weight is 20.2 kDa and the accession number is A0A7U3L5M7.
- ¥ 1950
规格
数量
FGF-21 Protein, Rat, Recombinant (His)
TMPY-07256
FGF-21 Protein, Rat, Recombinant (His) is expressed in HEK293 Cells. The accession number is Q8VI80.
- ¥ 3930
规格
数量
FGF-20 Protein, Rat, Recombinant (His & Myc)
TMPH-03292
Neurotrophic factor that regulates central nervous development and function. May play an important role in dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. FGF-20 Protein, Rat, Recombinant (His & Myc) is expressed in E. coli expression system with N-10xHis and C-Myc tag. The predicted molecular weight is 31.0 kDa and the accession number is Q9EST9.
- ¥ 1510
规格
数量
FGF-14 Protein, Human, Recombinant (isoform 1B)
TMPY-02804
FGF-14 Protein, Human, Recombinant (isoform 1B) is expressed in E. coli expression system. The predicted molecular weight is 21.1kDa and the accession number is Q92915-2.
- ¥ 2940
规格
数量
FGF-12 Protein, Canine, Recombinant
TMPY-03517
FGF12 is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and are involved in a variety of biological processes, including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth, and invasion. FGF12 lacks the N-terminal signal sequence present in most of the FGF family members, but it contains clusters of basic residues that have been demonstrated to act as a nuclear localization signal. When transfected into mammalian cells, FGF12 accumulated in the nucleus, but was not secreted. The specific function of FGF12 gene has not yet been determined. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been reported.
- ¥ 2940
规格
数量
FGF-15 Protein, Mouse, Recombinant (His & SUMO)
TMPH-02652
Involved in the suppression of bile acid biosynthesis through down-regulation of CYP7A1 expression.
- ¥ 1800
规格
数量
FGF-23 Protein, Rat, Recombinant (E. coli, His)
TMPH-03293
Regulator of phosphate homeostasis. Inhibits renal tubular phosphate transport by reducing SLC34A1 levels. Regulator of vitamin-D metabolism. Negatively regulates osteoblasts differentiation and matrix mineralization. Acts directly on the parathyroid to decrease PTH secretion. Upregulates EGR1 expression in the presence of KL.
- ¥ 1800
规格
数量
FGF-2 Protein, Chicken, Recombinant (His & Myc)
TMPH-00369
Acts as a ligand for FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3 and FGFR4. Also acts as an integrin ligand which is required for FGF2 signaling. Plays an important role in the regulation of cell survival, cell division, cell differentiation and cell migration. Functions as a potent mitogen in vitro. Can induce angiogenesis. FGF-2 Protein, Chicken, Recombinant (His & Myc) is expressed in E. coli expression system with N-10xHis and C-Myc tag. The predicted molecular weight is 23.8 kDa and the accession number is P48800.
- ¥ 2290
规格
数量
转到第1页
/ 2 页