- 全部删除
 您的购物车当前为空
您的购物车当前为空
NQO1 Protein, Human, Recombinant (His)
NQO1 gene is a member of the NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone) family and encodes a cytoplasmic 2-electron reductase. NQO1 forms homodimers and reduces quinones to hydroquinones. NQO1's enzymatic activity prevents the one-electron reduction of quinones that results in the production of radical species. Mutations in the NQO1 gene have been associated with tardive dyskinesia (TD), an increased risk of hematotoxicity after exposure to benzene, and susceptibility to various forms of cancer. Altered expression of NQO1 has been seen in many tumors and is also associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD). Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. Recent pharmacological research suggests the feasibility of genotype-directed redox chemotherapeutic intervention targeting NQO1 breast cancer, a common missense genotype encoding a functionally impaired NQO1 protein.

NQO1 Protein, Human, Recombinant (His)
| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 μg | ¥ 3,820 | 现货 |
产品信息
| 生物活性 | Activity testing is in progress. It is theoretically active, but we cannot guarantee it. If you require protein activity, we recommend choosing the eukaryotic expression version first. |
| 产品描述 | NQO1 gene is a member of the NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone) family and encodes a cytoplasmic 2-electron reductase. NQO1 forms homodimers and reduces quinones to hydroquinones. NQO1's enzymatic activity prevents the one-electron reduction of quinones that results in the production of radical species. Mutations in the NQO1 gene have been associated with tardive dyskinesia (TD), an increased risk of hematotoxicity after exposure to benzene, and susceptibility to various forms of cancer. Altered expression of NQO1 has been seen in many tumors and is also associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD). Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. Recent pharmacological research suggests the feasibility of genotype-directed redox chemotherapeutic intervention targeting NQO1 breast cancer, a common missense genotype encoding a functionally impaired NQO1 protein. |
| 种属 | Human |
| 表达系统 | E. coli |
| 标签 | N-His |
| 蛋白编号 | P15559-1 |
| 别名 | QR1,NMORI,NMOR1,NAD(P)H dehydrogenase, quinone 1,DTD,DIA4,DHQU |
| 蛋白构建 | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human NQO1 (P15559-1) (Met1-Lys274) was expressed with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. Predicted N terminal: His |
| 蛋白纯度 | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE 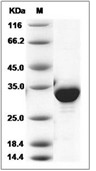 |
| 分子量 | 33 kDa (predicted); 33 kDa (reducing conditions) |
| 内毒素 | Please contact us for more information. |
| 缓冲液 | Lyophilized from a solution filtered through a 0.22 μm filter, containing PBS, pH 7.4. Typically, a mixture containing 5% to 8% trehalose, mannitol, and 0.01% Tween 80 is incorporated as a protective agent before lyophilization. |
| 复溶方法 | A Certificate of Analysis (CoA) containing reconstitution instructions is included with the products. Please refer to the CoA for detailed information. |
| 存储 | It is recommended to store recombinant proteins at -20°C to -80°C for future use. Lyophilized powders can be stably stored for over 12 months, while liquid products can be stored for 6-12 months at -80°C. For reconstituted protein solutions, the solution can be stored at -20°C to -80°C for at least 3 months. Please avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles and store products in aliquots. |
| 运输方式 | In general, Lyophilized powders are shipping with blue ice. |
| 研究背景 | NQO1 gene is a member of the NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone) family and encodes a cytoplasmic 2-electron reductase. NQO1 forms homodimers and reduces quinones to hydroquinones. NQO1's enzymatic activity prevents the one-electron reduction of quinones that results in the production of radical species. Mutations in the NQO1 gene have been associated with tardive dyskinesia (TD), an increased risk of hematotoxicity after exposure to benzene, and susceptibility to various forms of cancer. Altered expression of NQO1 has been seen in many tumors and is also associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD). Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. Recent pharmacological research suggests the feasibility of genotype-directed redox chemotherapeutic intervention targeting NQO1 breast cancer, a common missense genotype encoding a functionally impaired NQO1 protein. |




