- 全部删除
 您的购物车当前为空
您的购物车当前为空
GNE-3500
GNE-3500 is a Potent, Selective, and Orally Bioavailable Retinoic Acid Receptor-Related Orphan Receptor C (RORc or RORγ) Inverse Agonist. Retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor C (RORc, RORγ, or NR1F3) is a nuclear receptor that plays a major role in the production of interleukin (IL)-17. Considerable efforts have been directed toward the discovery of selective RORc inverse agonists as potential treatments of inflammatory diseases such as psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis. GNE-3500 possessed favorable RORc cellular potency with 75-fold selectivity for RORc over other ROR family members and >200-fold selectivity over 25 additional nuclear receptors in a cell assay panel. The favorable potency, selectivity, in vitro ADME properties, in vivo PK, and dose-dependent inhibition of IL-17 in a PK/PD model support the evaluation of GNE3500 in preclinical studies (J. Med. Chem., 2015, 58 (13), pp 5308–5322)
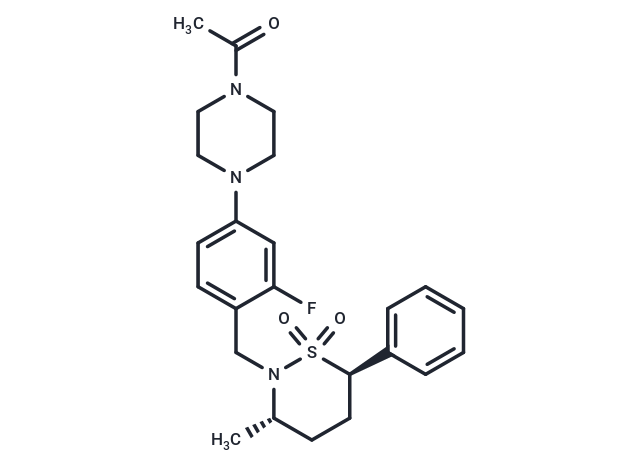
GNE-3500
GNE-3500 is a Potent, Selective, and Orally Bioavailable Retinoic Acid Receptor-Related Orphan Receptor C (RORc or RORγ) Inverse Agonist. Retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor C (RORc, RORγ, or NR1F3) is a nuclear receptor that plays a major role in the production of interleukin (IL)-17. Considerable efforts have been directed toward the discovery of selective RORc inverse agonists as potential treatments of inflammatory diseases such as psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis. GNE-3500 possessed favorable RORc cellular potency with 75-fold selectivity for RORc over other ROR family members and >200-fold selectivity over 25 additional nuclear receptors in a cell assay panel. The favorable potency, selectivity, in vitro ADME properties, in vivo PK, and dose-dependent inhibition of IL-17 in a PK/PD model support the evaluation of GNE3500 in preclinical studies (J. Med. Chem., 2015, 58 (13), pp 5308–5322)
| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | ¥ 10,600 | 6-8周 | |
| 50 mg | ¥ 13,800 | 6-8周 | |
| 100 mg | ¥ 17,500 | 6-8周 |
产品介绍
| 产品描述 | GNE-3500 is a Potent, Selective, and Orally Bioavailable Retinoic Acid Receptor-Related Orphan Receptor C (RORc or RORγ) Inverse Agonist. Retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor C (RORc, RORγ, or NR1F3) is a nuclear receptor that plays a major role in the production of interleukin (IL)-17. Considerable efforts have been directed toward the discovery of selective RORc inverse agonists as potential treatments of inflammatory diseases such as psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis. GNE-3500 possessed favorable RORc cellular potency with 75-fold selectivity for RORc over other ROR family members and >200-fold selectivity over 25 additional nuclear receptors in a cell assay panel. The favorable potency, selectivity, in vitro ADME properties, in vivo PK, and dose-dependent inhibition of IL-17 in a PK/PD model support the evaluation of GNE3500 in preclinical studies (J. Med. Chem., 2015, 58 (13), pp 5308–5322) |
| 分子量 | 459.58 |
| 分子式 | C24H30FN3O3S |
| CAS No. | 1537859-24-7 |
| 存储 | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. |





 还可以
还可以

评论内容