- 全部删除
 您的购物车当前为空
您的购物车当前为空
(±)11(12)-EpETE
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) is metabolized into epoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (EpETE) by multiple cytochrome P450 isoforms. The predominant compound of this epoxygenase pathway, (±)17(18)-EpETE, induces relaxation in vascular and airway smooth muscles through its action on large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BKCa) channels, specifically by binding to the BKα channel subunits. Another notable epoxygenase pathway derivative, (±)11(12)-EpETE, also generated from EPA via CYP450 activity in both in vitro and in vivo studies, has biological and physiological roles that are yet to be fully elucidated.
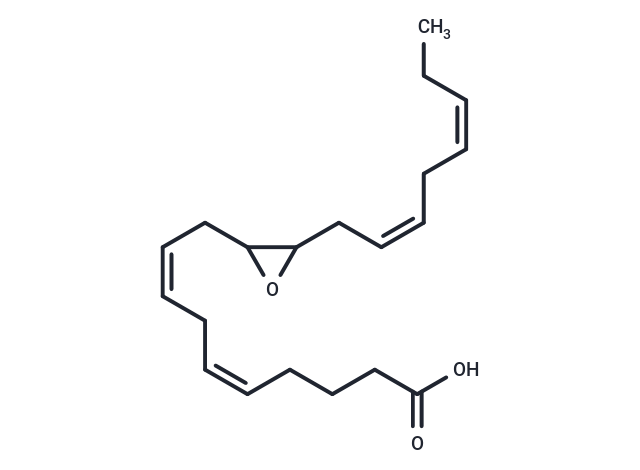
(±)11(12)-EpETE
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) is metabolized into epoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (EpETE) by multiple cytochrome P450 isoforms. The predominant compound of this epoxygenase pathway, (±)17(18)-EpETE, induces relaxation in vascular and airway smooth muscles through its action on large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BKCa) channels, specifically by binding to the BKα channel subunits. Another notable epoxygenase pathway derivative, (±)11(12)-EpETE, also generated from EPA via CYP450 activity in both in vitro and in vivo studies, has biological and physiological roles that are yet to be fully elucidated.
| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg | 待询 | 8-10周 | |
| 50 mg | 待询 | 8-10周 |
产品介绍
| 产品描述 | Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) is metabolized into epoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (EpETE) by multiple cytochrome P450 isoforms. The predominant compound of this epoxygenase pathway, (±)17(18)-EpETE, induces relaxation in vascular and airway smooth muscles through its action on large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BKCa) channels, specifically by binding to the BKα channel subunits. Another notable epoxygenase pathway derivative, (±)11(12)-EpETE, also generated from EPA via CYP450 activity in both in vitro and in vivo studies, has biological and physiological roles that are yet to be fully elucidated. |
| 别名 | (±)11,12-EEQ |
| 分子量 | 318.5 |
| 分子式 | C20H30O3 |
| CAS No. | 504435-15-8 |
| 存储 | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. |





 还可以
还可以

评论内容